- Industry insights
- People in tech
- Tech trends at BEECODED
- 14 Mar 2025
Beyond Encryption: Advanced Strategies to Prevent Data Breaches in SaaS Applications
According to 1asig.ro, cybersecurity experts estimate that cyberattacks that occur every day cost 8.44 trillion dollars.



Table of contents
Contributors

Introduction
According to 1asig.ro, cybersecurity experts estimate that cyberattacks that occur every day cost 8.44 trillion dollars, a figure expected to rise to around 24 trillion dollars by 2027. These amounts make us all agree that applying advanced protection strategies for data breaches in SaaS is extremely important, as they can cause a major negative impact on business, both financially and in terms of customer trust and brand reputation.
Read our guide below to learn about the advanced measures you can implement to strengthen the security of your SaaS infrastructure.
Statistics on Data Breaches in SaaS Platforms
Several types of cyber-attacks can affect a SaaS platform, including phishing, data scraping, ransomware, API exploitation, and many others. The most common cyberattacks on SaaS applications globally are phishing and ransomware.
According to DNSC (National Directorate for Cyber Security), the most common attacks in Romania are ransomware, DDoS, and phishing. These three types of attacks will be detailed below.
3 Types of Cyberattacks with Real-World Examples
- Phishing
According to sentinelone.com, cloud security statistics show that 51% of organizations reported that phishing is one of the most common types of attacks launched by malicious actors to steal cloud security data.
One of the most famous examples of phishing took place between 2013 and 2015, when Facebook and Google lost 100 million dollars in this type of scam. The attacker sent fake invoices, pretending to be Quanta, a joint supplier of the two companies. Unfortunately, both companies paid the bills without realizing they were victims of phishing.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attacks
In DDoS, the attackers use a network of compromised computers to overwhelm the servers of a SaaS platform with traffic, causing disruption of service. In 2018, GitHub was the victim of the largest DDoS attack in history, with 1.35 Tbps of traffic affecting the platform for about 10 minutes.
- Ransomware
In this type of attack, hackers encrypt your cloud files and demand money to unlock them. A famous example of a ransomware attack is WannaCry, which took place in May 2017. WannaCry affected more than 200,000 computers in more than 150 countries. The ransomware exploited a vulnerability in Windows systems to encrypt victims’ files and demand a ransom in Bitcoin.
The attack had a massive impact, and many organizations were forced to shut down due to the encrypted files. It was also a great lesson on the importance of updating software to prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited.
Insider Threats
Threats do not only come from outside; they can also come from within. Internal threats refer to employees or collaborators who have access to sensitive SaaS application data and can misuse it for malicious purposes.
For example, in 2022, a former Yahoo employee was accused of stealing 570,000 files, including the advertising engine’s source code, which he transferred to personal external devices to sell to a competitor, The Trade Desk.
In the following section, we will discuss how you can implement several strategies that will help you prevent these security breaches in SaaS applications.
Implementing Defense-in-Depth to Mitigate Data Breaches in SaaS Apps
Defense in depth is a cybersecurity strategy that involves the use of multiple layers of protection to defend information and resources. The main idea is that if one security layer fails, the others will continue to protect the system.
To effectively implement this strategy in the SaaS context, it is recommended to focus on the following aspects:
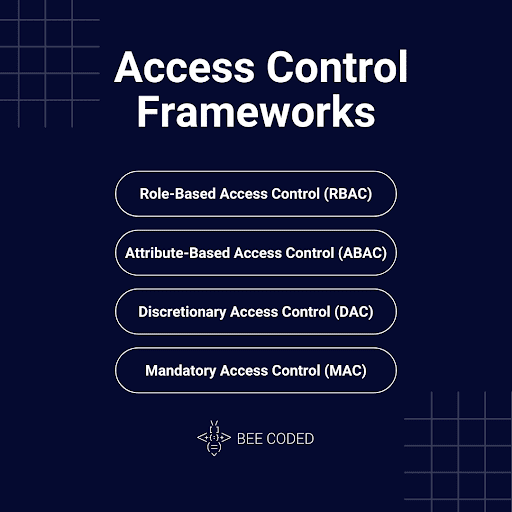
1. Access Control Frameworks
Access control frameworks are sets of rules, policies, and mechanisms used to control user access to the resources of a system or application. These frameworks define who can access what resources and in what way, thus ensuring the protection of data and systems from unauthorized access.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This refers to assigning specific permissions based on user role, ensuring that each person only has access to the information needed for their job.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): ABAC relies on user attributes (such as age, location, or time of access) and resource attributes to decide access.
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC): DAC allows resource owners to decide who has permission to access their resources.
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC): In MAC, access to resources is controlled by strict policies set by an administrator, and users can’t change these rules.
It is also important to implement robust authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA).
 Role-Based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control
2. API Security Measures
- Data Encryption: Protect your data by using TLS protocols to keep it safe during transit and prevent unauthorized access.
- API Activity Monitoring and Logging: Track and log API usage to detect suspicious activity and respond quickly to potential threats.
- Updating and patching APIs frequently: APIs need to be updated and patched regularly to prevent security issues. Establish a regular check plan and apply available updates immediately.
- Validate and Clean All Inputs: Check each input to make sure it follows the correct format. Use tools like Validator.js to prevent attacks.
3. Secure Development Practices
- Integrating Security into the Development Process: Adopt a development framework (DevSecOps) that includes security assessments at every stage, from planning through implementation and maintenance.
Find more about implementing security in the software development lifecycle in our article here:
- Continuous Security Testing and Assessment: Conduct penetration tests and security audits to identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
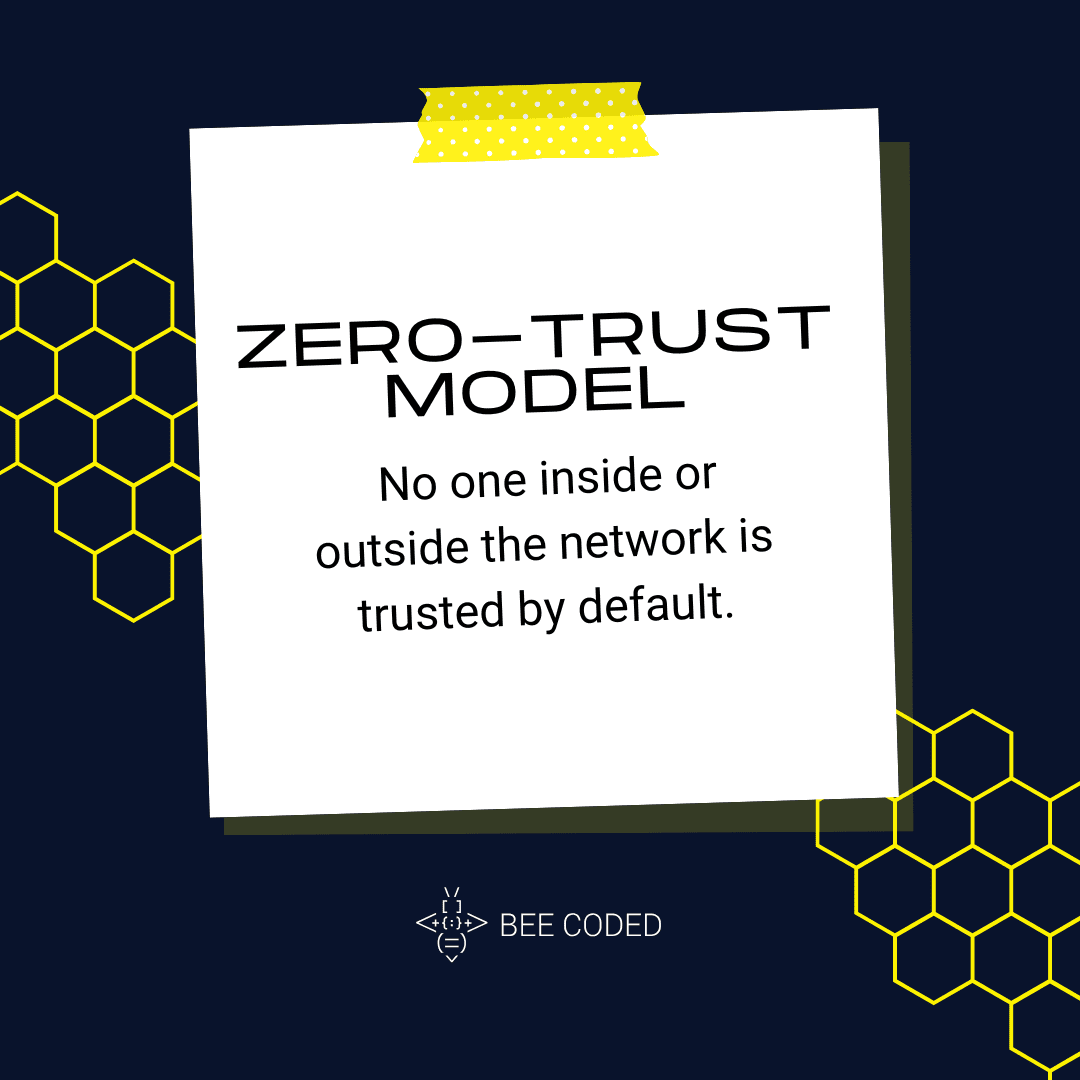
- Implement a Zero-Trust model where no one, inside or outside the network, is trusted by default. All access requests are authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated, regardless of the source. Zero-Trust helps resolve configuration issues early, reducing the risk of breaches, and it will, therefore, become a standard practice in SaaS environments.
 Zero-Trust model – data breaches in saas
Zero-Trust model – data breaches in saas
No one inside or outside the network is trusted by default.
- Trust is never assumed.
- Every access request is verified.
- Access is constantly monitored and reassessed.
Effective Threat Monitoring and Incident Response Planning
By using Zero-Trust principles, you can ensure better control and rapid attack detection. Also, through a series of specific steps, you can build an effective monitoring and response plan:
 Zero-Trust principles – data breaches in saas
Zero-Trust principles – data breaches in saas
Conclusions
In conclusion, security breaches can have a major impact on business. Keep in mind that a proactive approach, with continuous monitoring and regular updates, can protect you from potential attacks and ensure the long-term security of your infrastructure.
Let’s work together to strengthen your SaaS security. Get in touch for personalized, hands-on advice!
12 Natural Language Processing techniques used to process text by data scientists
What is natural language generation? (NLG)
What is natural language processing (NLP)?